As a part of the EKKIRA project LAB University of Applied Sciences works in tight cooperation with a network of local organizations, most notably construction firms and IoT infrastructure providers to build a long-lasting digital ecosystem. In the future this ecosystem can be adopted to inform, train and otherwise utilize digital solutions in order to improve resource productivity and sustainability in the South Karelia region. (EKKIRA 2022.)
The process of implementation of Digital Twin solutions
One of the practical goals set by the EKKIRA project is the development of Digital Twin pilots and creation of testing environments for two physical buildings: Mioni Campus in Imatra operated by Mitra Oy and LOAS Theater in Lappeenranta. The term ‘Digital Twin’ in this case refers to a virtual representation of the building achieved with usage of Internet of Things (IoT), Augmented Reality (AR), Artificial Intelligence (AI) and cloud technologies. (EKKIRA 2022.)
The process of digital twin creation contains two main parts. The first is development of a functional 3D model for each building with a graphical user interface that shows all IoT devices currently connected and active. This part is modeled with Unity 3D Engine and receives the data from the IoT sensors through Microsoft Azure Cloud infrastructure.
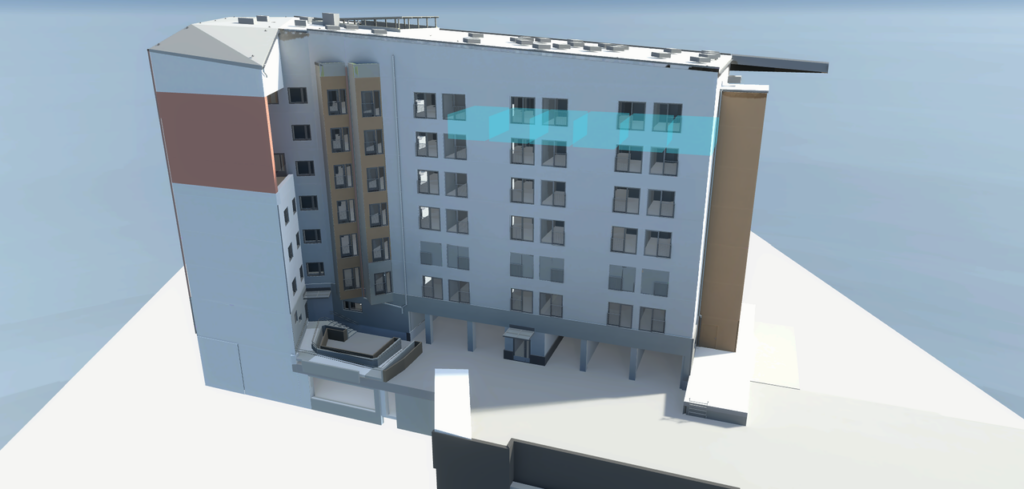

The second part is the laser scanning based AR simulation of floors, inner spaces and other related components of each building. AR implementation is a separate process running on its own schedule separated from Unity 3D development but it also uses the same sources of data to confirm that its information model is fully comparable to the original building.
About Azure cloud services in EKKIRA project
The purpose of Azure Cloud in EKKIRA project is to enable reliable transfer of telemetry data between physically connected IoT devices inside the buildings and frontend Unity application (with possibility to connect AR application in the future). The different Azure Cloud services are used to handle communication with IoT devices, receive and process device-to-cloud messages and deliver the data to the database (from where it can be accessed by the client application) in safe and reliable manner.
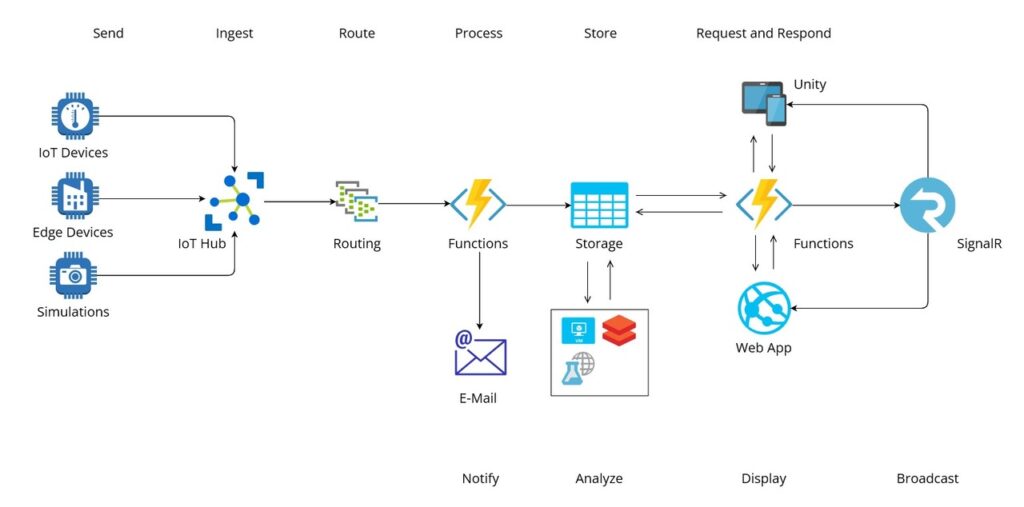
The cloud infrastructure is designed to be highly reactive, which means it reacts accordingly to incoming events be it IoT telemetry, alarms or data requests from the frontend application. As the image above shows, the logical flow of events can be described in simple verbs. The telemetry data is first sent by device, then ingested, routed, processed, stored and finally requested by the client. These operations cover the core functionality of cloud infrastructure.
The development of digital twin pilots and Azure Cloud infrastructure will continue further in 2022 and 2023 as the network of participating organizations keeps growing larger. It is also expected that the infrastructure will continue to function after the project ends.
Author
Jevgeni Anttonen works as a LAB Digital Team member at LAB University of Applied Sciences. He participates in the CB-Safe and EKKIRA projects.
References
EKKIRA. 2022. Digitaaliset ratkaisut rakennetun ympäristön resurssituottavuudessa. Project. Cited 17 Jun 2022. Available at https://lab.fi/fi/EKKIRA